Did you know that nearly 85% of people between 12 and 24 get some acne? This fact shows how common acne is among young people. It introduces us to the complex journey of acne development. This article will walk you through these stages. You’ll learn how acne evolves from small spots to big breakouts.
It’s crucial to understand the life cycle of a pimple for better skin management. This cycle starts with things that make sebum production go up. It goes through various stages, each impacting skin health. By diving into each stage, you’ll spot symptoms and learn how to prevent and treat them. For more, visit stages of acne development.
Key Takeaways
- 85% of young individuals will experience acne at some point.
- Understanding acne’s stages helps in effective management.
- The acne formation process starts with sebum overproduction.
- Recognizing early symptoms can prevent severe breakouts.
- Timely treatment can improve overall skin health.
Understanding Acne: An Overview
Acne is a common skin issue that many people face. This guide sheds light on what acne is and how it happens. It starts when hair follicles get blocked by oil and dead skin. Various factors, like hormonal changes during teen years, can increase oil production, causing acne.
What is Acne?
Acne appears as spots, pimples, or cysts on the face, back, and shoulders. It happens when pores get clogged and inflamed. To know acne, we must look at its different impacts. Genetics, the environment, and how we live can all play a role.
Why Do Some People Get Acne?
Teens are more likely to get acne because of hormone changes. This is a key reason it’s more common in young people. Studies reveal that up to 85% of people will face acne at some time. Diet, stress, and certain meds can also make acne worse, showing how complex it is.
The Stages of Acne Development
It’s important to know the stages of acne for effective treatment. Early identification of the stage can help start the right treatment soon. This makes a big difference in how well the treatment works and the health of the skin.
The Importance of Recognizing Each Stage
Knowing the unique signs of each acne stage is key. This knowledge lets people choose the best care for their skin. The main stages are:
| Stage | Description | Common Treatments |
|---|---|---|
| Comedonal | Characterized by blackheads and whiteheads; non-inflammatory. | Exfoliants, topical retinoids. |
| Inflammatory | Includes papules and pustules; redness and swelling present. | Topical antibiotics, oral antibiotics. |
| Post-inflammatory | Marked by redness or dark spots after acne heals. | Lightening agents, chemical peels. |
| Cystic | Severe form; painful, deep nodules or cysts that often require dermatological intervention. | Isotretinoin, corticosteroid injections. |
Understanding acne’s stages helps in picking the right treatment. For more info, visit the different stages of acne. This knowledge is a big step towards healthier skin.
The Acne Formation Process
It’s important to understand how acne starts to treat this common skin issue. It often begins with sebum overproduction, caused by hormone changes. This makes the sebaceous glands too active. They make more oil, leading to clogged pores.
How Acne Begins with Sebum Overproduction
This increased oil sets the stage for acne. Hormones, especially during puberty, greatly affect this. They cause glands to make more oil. This mixes with dead skin and debris, causing a block in the hair follicles. Understanding this is key to tackling more severe acne later.
The Role of Follicular Obstruction
After too much sebum is made, follicular obstruction is the next issue. Clogged follicles trap bacteria, creating a space without air. This leads to more severe acne and inflammation. Knowing how these factors work together helps in finding effective treatments, as discussed here.
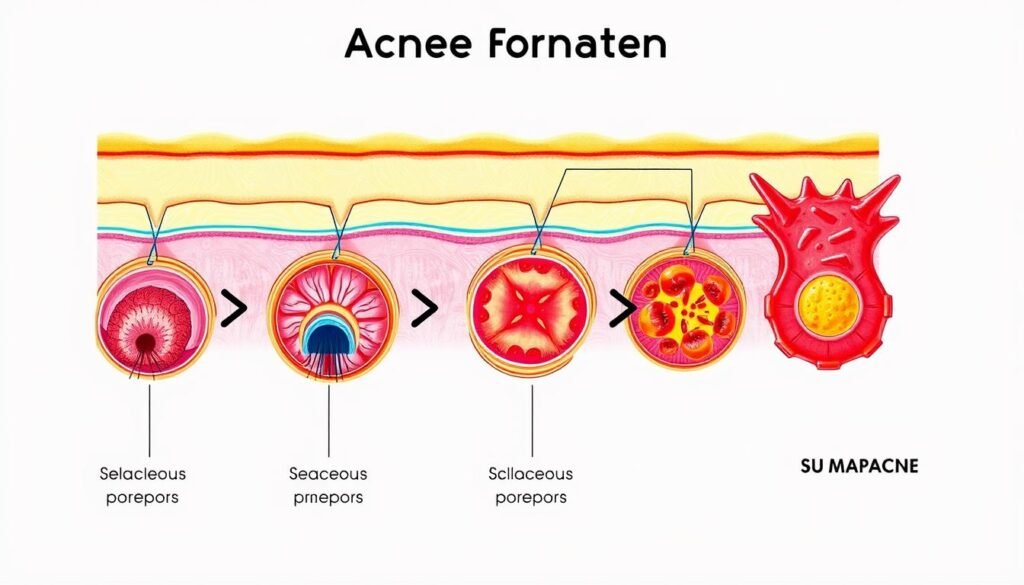
Comedones: The Initial Stage
Comedones are the first stage of acne, acting as a sign of worse acne to come. There are two main types: blackheads and whiteheads. They look different and have unique features. Knowing about them helps manage and stop acne from getting worse.
What Are Blackheads and Whiteheads?
Blackheads, or open comedones, form when hair follicles get blocked with sebum and dead skin. Since they’re open to the air, they turn dark. Whiteheads, or closed comedones, are when the blockage stays under the skin. They look like small, flesh-colored bumps. Both are early forms of acne and can turn into more serious blemishes if ignored.
Factors Contributing to Comedone Formation
Several factors can cause comedones, including:
- Hormonal fluctuations: Changes in hormones, like during puberty or menstruation, can make more sebum. This extra oil can block follicles.
- Diet: Eating a lot of sugars and dairy might make comedones worse. These foods affect your insulin and hormones.
- Environmental factors: Pollution can leave oil and dirt on the skin. This messes with how skin cells renew and can clog pores.
| Type of Comedone | Characteristics | Appearance |
|---|---|---|
| Blackheads | Open follicle filled with sebum and dead skin | Dark or black surface due to oxidation |
| Whiteheads | Closed follicle with trapped sebum and dead skin | Flesh-colored or white bump beneath the skin |
Knowing the early signs of acne helps people act early in their skincare routines. This can stop worse types of acne from developing.
Inflammatory Lesions: Escalation of Acne
Acne can get worse, moving from simple comedones to inflammatory lesions like papules and pustules. Knowing how this happens is key for people to treat their acne effectively. Inflammatory lesions stand out because they’re red, swollen, and might have pus.
Understanding Papules and Pustules
Papules are small, raised spots on the skin showing early signs of inflammation. They can be sore and show how the body’s immune system is reacting. Pustules are like papules but have pus inside, making them look white or yellow at the tip. Both types are signs of a strong reaction to bacteria, including Propionibacterium acnes.
How Inflammation Develops in Acne
The development of inflammation in acne is key. Bacteria grow in clogged pores, leading to an immune response. This makes more blood flow to the area, causing redness and swelling. When papules and pustules appear, it means acne is getting severe, showing the need for special treatments.
| Type of Lesion | Characteristics | Common Treatments |
|---|---|---|
| Papules | Raised, red bumps, no pus | Topical retinoids, benzoyl peroxide |
| Pustules | Filled with pus, red base | Topical antibiotics, oral medications |
Acne Pathogenesis: The Biological Mechanisms
Understanding acne’s underlying processes makes its complexity clear. It shows why acne severity varies among individuals. The interaction of biological factors is key.
The Role of Bacteria in Acne Development
The role of bacteria, especially Propionibacterium acnes, is crucial in acne. This bacterium thrives in clogged hair follicles. It produces substances that inflame and redden the skin.
Research shows that treatments targeting this bacteria can help. It proves how important these microbes are for skin health.
Genetic Factors and Hormonal Changes
Genetics play a big part in acne risk. People with a family history of severe acne have a higher risk. Hormones also affect acne, especially during puberty or menstrual cycles.
These hormonal shifts increase oil production, leading to acne. For more details on acne biology, check this article.

Follicular Rupture: The Turning Point
Follicular rupture is a key moment in how acne progresses. Knowing what happens at this stage sheds light on achieving healthier skin. When a follicle breaks, it lets out its contents into the skin around it. This can lead to a big immune reaction.
What Happens During Follicular Rupture?
The break lets sebum, bacteria, and dead skin cells enter the dermis. This mix triggers inflammation. Immune cells rush to fight off what they see as a threat. This can worsen the situation and cause cystic acne to form. The way our body reacts to the rupture can make acne worse.
Consequences of Follicular Damage on Skin Health
The effects on skin health after a follicle ruptures can be serious. This includes inflammation that can lead to scars and dark spots. Managing what causes follicular rupture can help lessen these bad outcomes. If you want to keep your skin healthy, think about how to avoid these triggers. For more info on how acne develops, check out this resource.
Prevention and Treatment Strategies
It’s crucial to prevent and treat acne to keep your skin healthy. Understanding the different stages of acne helps. This way, you can use the right strategies to avoid breakouts. Mixing changes in your lifestyle with specific treatments is often effective.
Preventive Measures Against Acne Development
Stopping acne before it starts means being proactive. Here are the key actions:
- Balanced diet: Eating lots of fruits, veggies, and whole grains keeps your skin happy.
- Proper skincare: Use gentle cleansers and moisturizers regularly to avoid clogging your pores.
- Lifestyle choices: Exercise often, get enough sleep, and manage stress to keep acne away.
Effective Treatment Options for Different Stages
Choosing the right treatment for each acne stage is key. Here are some common approaches:
| Acne Stage | Treatment Options |
|---|---|
| Comedones | Topical retinoids, such as tretinoin or adapalene. |
| Inflammatory lesions | Topical or oral antibiotics, benzoyl peroxide. |
| Cysts | Isotretinoin for severe cases; corticosteroid injections for inflammatory cysts. |
Conclusion
Knowing how acne develops is key to managing and treating it correctly. Acne starts as comedones and can get worse, turning into cystic lesions. Recognizing the signs early helps people act fast. They can pick treatments that work best for them.
Acne varies from person to person because different factors cause it for everyone. Finding the right treatment early can stop worse problems. That’s why consulting a skin care expert is crucial. Learning about acne helps people make smart choices for their skin.
Understanding acne and how to treat it lets individuals control their skin health. This knowledge improves how people manage acne. It also boosts their confidence in how they look.