Did you know about 85% of young people ages 12 to 24 get acne? This shows acne is a common issue for many, leading to emotional and psychological struggles. This article dives into acne science, answering common questions and showing its effects on individuals.
This exploration includes biological causes and compares old and new treatment methods. It combines dermatology research with new tech, like natural language processing. The goal is to give readers insightful and useful knowledge.
Key Takeaways
- Acne affects a significant percentage of adolescents, highlighting the need for comprehensive understanding.
- Scientific research continues to uncover the underlying causes of acne.
- Common misconceptions about acne can hinder effective treatment options.
- Integrating technology into dermatological studies enhances our understanding of acne.
- Effective acne treatment often involves a combination of therapies.
Understanding Acne: An Overview
Acne is a big worry for many, known as a long-lasting skin issue that harms skin health. Understanding acne means knowing its types. It appears as different lesions, split into acne vulgaris and cystic acne. Knowing the difference is key for the right treatment.
About 85% of people will deal with acne at some point. This shows how common it is among different people and ages. Especially in teen years, hormones trigger acne, but adults can face it too, even after thirty.
To truly get acne, it’s important to know its causes and clear up myths. It’s seen as a teen problem, but it actually touches many, no matter their age. Experts stress looking at skin issues more broadly.
With a full acne overview, people can better tackle this common skin issue. Knowledge leads to wise choices about treatment, helping skin stay healthy.
The Biology Behind Acne Formation
To grasp acne’s complexity, we dive into the acne biology that fuels its start. Acne mainly starts in the pilosebaceous unit, which has hair follicles and sebaceous glands. These glands produce sebum, a crucial oil for skin health. When hormones spike, they can make too much sebum. This mixes with dead skin, causing clogged pores.
The bacterium Cutibacterium acnes worsens acne by thriving in clogged pores. This leads to inflammation. The immune system fights this bacteria, creating the red, inflamed spots known as acne. Genetics and puberty hormones can make this worse.
Stress and what we eat also affect acne. Stress can make the glands produce more oil. These elements combine to form the full picture of acne formation.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Sebum Production | Excess sebum caused by hormonal changes leads to clogged pores. |
| Dead Skin Cells | Accumulation of dead skin cells further contributes to pore blockage. |
| Cutibacterium acnes | Bacteria that thrive in clogged pores, causing inflammation. |
| Genetic Predisposition | Family history may increase the likelihood of acne development. |
| External Factors | Stress and diet can exacerbate acne symptoms. |
Understanding acne’s underlying causes helps in finding effective treatments and preventive measures. For deeper details, check out the studies at the National Center for Biotechnology Information.

Research and FAQs:
Researchers focus a lot on finding out what causes acne. This skin problem can come from hormones, what you eat, and your genes. Lately, they’re also looking into how stress might make acne worse. This means checking if stress hormones, like cortisol, harm skin health. Big hormone changes, like those during puberty or periods, can also make acne more severe.
What Causes Acne?
The table below shows the main causes of acne, as current studies suggest:
| Causes | Description |
|---|---|
| Hormonal Imbalances | Changes in hormones can increase oil production in the skin. |
| Dietary Influences | Foods high in sugar and dairy may worsen acne. |
| Genetic Factors | Your family history might make you more prone to acne. |
| Environmental Factors | Bad air quality can irritate your skin. |
| Stress | Being stressed can cause swelling and redness in the skin. |
Common Misconceptions About Acne
Many myths about acne can lead to confusion. Let’s clear up some common false beliefs with research:
- Chocolate Causes Acne: Research shows there’s no direct link.
- Pore-clogging Products Are Always Bad: Not all oils or skincare items will cause acne.
- You Only Get Acne During Puberty: People of any age can get acne.
- Hygiene Is the Main Factor: Washing too much could actually make your skin worse.
Types of Acne: A Detailed Guide
It’s important to know the different types of acne to treat it well. Each kind shows its own signs and needs a special treatment plan.
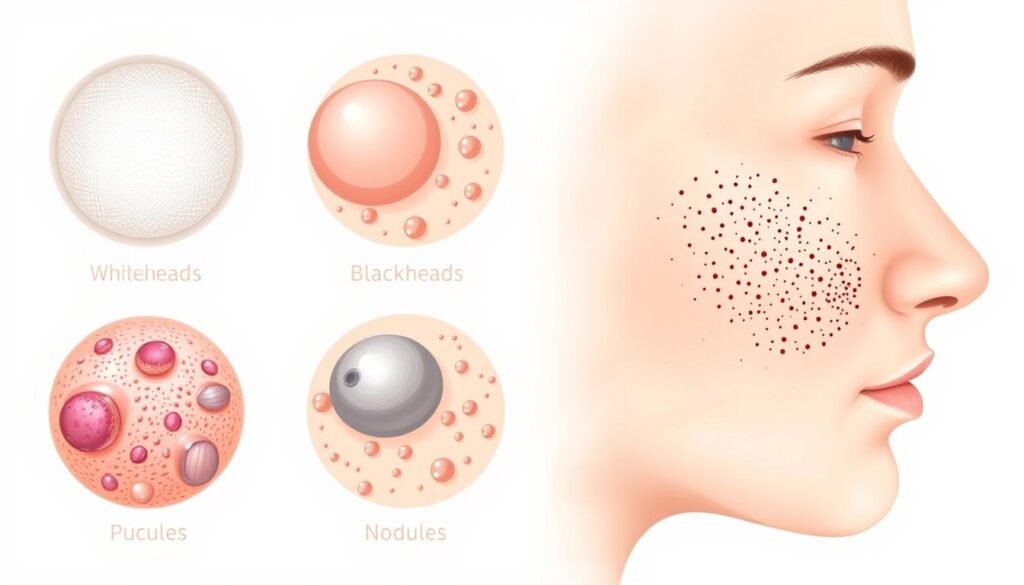
Acne vulgaris is the most common type, seen in teenagers. It shows up as blackheads, whiteheads, and pustules. Usually, simple treatments work, but some cases might need more help.
Cystic acne is a tougher form, causing deep, sore bumps under the skin. These can scar without the right treatment. People with this acne type should get professional advice.
Nodular acne is similar to cystic acne but has bigger, harder bumps. Prescriptions or expert care might be needed to control it and avoid harm to the skin.
Acne mechanica comes from rubbing or heat, common in athletes or if you wear tight clothes. Knowing these types of acne helps with correct diagnosis and finding the right treatment plan. For more info on acne, check out this resource.
Natural Language Processing in Acne Research
Natural language processing (NLP) has changed the game in dermatology, especially for acne. It lets doctors look at big amounts of data to spot trends. This helps them improve how they care for patients. Using NLP means they can understand patient stories and how they react to treatments better.
Now, researchers are really into using NLP for acne research techniques. They dig into what patients say about their symptoms and treatments. This is key for seeing how different treatments work for different people. Being able to analyze lots of texts helps them get the full picture of acne and how treatments work.
Better NLP models mean better ways to talk about acne care. Healthcare workers can make their advice fit what patients commonly worry about. For instance, some automated systems now talk in a caring way about acne causes and treatments. They got good results, like one chatbot tool that’s great at giving out info here.
In essence, NLP in acne research is making patient care better. It also helps doctors understand acne management deeply because of advanced data analysis. Thanks to cutting-edge NLP, dermatology’s future is looking up. It’s leading to new research possibilities and better ways to talk with patients.
Text Analysis Techniques in Dermatology
Dermatology now uses cutting-edge tech to fight skin issues, like acne. Text analysis is key in understanding acne with new techniques. As we get more data, we must accurately interpret it. This leads to better ways to study acne.
How Machine Learning is Impacting Acne Studies
Machine learning gives a new edge to acne research. It lets us dive deep into large datasets from health records and studies. By using algorithms, researchers can spot patterns, foresee outbreaks, and customize treatments. This means they can look through thousands of cases quickly. Machine learning is making acne treatment more scientific.
Role of Computational Linguistics in Acne Data
Computational linguistics is crucial. It helps process feedback from patients and data from acne forums. It turns complex text into something we can study. This lets doctors understand what patients really experience. It makes sure patient needs and clinical research connect. For more details, check out this informative source.
| Technique | Description | Application in Acne |
|---|---|---|
| Text Mining | Extracting insights from unstructured text data. | Identifying common concerns and symptoms reported by patients. |
| Sentiment Analysis | Evaluating patient feedback to gauge satisfaction. | Understanding treatment effectiveness and patient emotions. |
| Predictive Modeling | Using historical data to predict future outcomes. | Forecasting acne outbreaks based on previous medical history. |
These methods are changing the game in dermatology. They make sure acne treatment is focused on data and patient needs.
Effective Treatments: What Science Suggests
Acne can really affect how we feel about ourselves. There are many acne treatments to pick from, depending on your skin and what you like. Science behind acne treatment looks into different methods, including creams and pills.
Topical solutions are popular. They have things like benzoyl peroxide and retinoids. These target the main problems causing acne, such as too much oil and blocked pores. They also have ingredients to fight off germs and heal your skin, which doctors like.
For tougher acne, oral antibiotics and hormones can help. Your treatment should match your acne type and how serious it is. Mixing medicine with other treatments works well for many people.
New treatments are being talked about a lot. Light therapy is interesting because it helps reduce swelling and kill off bacteria. Scientists are also looking into biologics for more customized treatments.
Talking to a doctor is key to find the right acne solution. Using trusted sources, like this study, helps you understand your options better. Checking out old and new treatments can change the way we deal with acne. For more info on acne issues and effective treatments, see this resource.
Home Remedies vs. Medical Therapies
The debate over home remedies and medical treatments for acne is important. People often try natural methods like tea tree oil and aloe vera. They are drawn to these for their gentleness and easy access.
However, these remedies lack scientific support and detailed research. This support and research are key to formal medical treatments. Medical treatments for acne, including topical retinoids and benzoyl peroxide, are well-studied. This means talking to healthcare professionals is beneficial. They can offer treatments suited to your skin type and acne severity.
These treatments are not only more successful but also target acne’s root causes. On the other hand, home remedies can be an additional help. Yet, relying only on them might slow down getting the right treatment.
Knowing the pros and cons of both approaches is vital. It helps people make smart choices for their acne care. This is essential for clear, healthy skin.