Did you know over 85% of teenagers experience acne at some point? It’s not just for teens; adults get forehead acne too. The reasons for forehead acne vary greatly. They include hormone changes, genetics, stress, and the environment. This article will explore the main factors behind forehead acne. We’ll see how these triggers connect with each other.
Key Takeaways
- Forehead acne is prevalent among teenagers but can persist into adulthood.
- Family history plays a vital role in acne development.
- Hormonal changes, especially during puberty, can lead to increased outbreaks.
- Stress and dietary habits may influence the occurrence of forehead acne.
- Environmental factors like humidity and pollution can exacerbate the condition.
- Maintaining hygiene is crucial for preventing forehead acne.
Understanding Acne and Its Types
Acne is a skin issue that affects many people, creating confusion about its causes and how to deal with it. Knowing different acne types helps find the right treatments. Getting to the root of acne is key in finding the effective ways to manage it.
Overview of the Causes
Acne starts when sebaceous glands get blocked. These glands produce sebum, which keeps the skin moist. But when sebum gets trapped with dead skin and bacteria, it blocks the pores. This blockage can lead to different kinds of acne:
- Comedonal acne: Shows up as blackheads or whiteheads. It’s usually not too red or swollen.
- Inflammatory acne: Causes red, swollen pimples. This happens when the body fights bacteria in the clogged pores.
- Nodular/cystic acne: This serious type creates deep, painful bumps under the skin. Treating this acne might need stronger methods.
Several things can make acne worse. Genetics can be a factor, as some people have naturally more active sebaceous glands. Changes in hormones, like testosterone or menstrual cycles, also play a role. They can make the body produce more sebum. Certain medications like steroids and anticonvulsants can also increase acne risk.
Diet and stress have a big impact on acne. Eating foods with a high glycemic index can cause more acne. Stress, like from exams or big life changes, can also make acne worse. Research supports this idea.
To learn more about acne and the different acne types, look into treatments. There are both creams and pills that can help. For trusted advice, the Cleveland Clinic is a great resource.
What Causes Forehead Acne?
Many people deal with forehead acne. It happens for various reasons. Knowing why can help treat and prevent it. This part will look at what causes it and the types of acne that appear on the forehead.
Overview of the Causes
Forehead acne mainly comes from blocked hair follicles and sebaceous glands. This happens due to too much sebum, bacteria, or dead skin cells. The forehead has more sebaceous glands, especially in the T-zone. Because of this, acne lesions often form there, triggered by different factors:
- Hormonal changes: Changes during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause can make more oil and cause acne.
- Stress: Stress can make acne worse, including on the forehead.
- Products: Some hair products, medicines, and makeup can irritate skin and cause breakouts on the forehead.
- Hygiene: Not cleaning your skin well can lead to forehead acne by leaving oil and dirt.
Different Types of Acne on the Forehead
Forehead acne shows up in many ways, like:
| Acne Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Closed Comedones (Whiteheads) | Small, flesh-colored bumps from clogged follicles. |
| Open Comedones (Blackheads) | Whiteheads that turn dark when exposed to air. |
| Papules | Small, red, raised bumps that can be tender. |
| Pustules | Red, pus-filled bumps, often called “zits.” |
| Nodular Acne | Hard lumps under the skin that hurt and need serious treatment. |
| Cystic Acne | Big, painful cysts that can scar. |
Knowing the type of forehead acne you have helps find the right treatment. It helps keep the skin healthy and clear.
The Role of Hormonal Imbalance
Hormones and acne have a complex link, important for skin health. Hormonal imbalances play a big role in acne, affecting many people. Hormonal levels cause acne flare-ups for many, especially during puberty.
How Hormones Affect Acne
Hormones are key in acne development. Puberty increases androgen levels, boosting skin oil production. This oil, with dead skin, clogs pores, leading to acne. For women, hormonal changes during menstrual cycles, pregnancy, and menopause add to the problem. Research finds that hormonal acne, common in women, often shows as cysts or nodules. This acne mainly appears around the jawline and chin, but sometimes the forehead too.
Puberty and Hormonal Changes
Puberty brings big hormonal changes, affecting many teens. About 80% of people from 11 to 30 will face acne, often hormonal acne, during these years. Estrogen and progesterone changes also play a role in acne. This issue can extend into adulthood, impacting many women past their teens due to hormonal changes. Surprisingly, 50% of women aged 20-29 face acne, showing the need for awareness and treatments focusing on hormonal balance.
| Age Group | Percentage Experiencing Acne | Common Trigger Hormones |
|---|---|---|
| Teens (11-19) | 80% | Androgens |
| Young Adults (20-29) | 50% (Women) | Estrogen, Progesterone |
| Adults (40-49) | 25% (Women) | Androgens |
| Overall Adult Population (20-40) | 40-50% | All Hormones |
Clogged Pores: A Major Culprit
Forehead acne typically appears because of clogged pores. This problem arises when too much oil and dead skin cells build up. To keep skin clear, it’s key to understand how oil and skin cells lead to breakouts.
Excess Oil and Dead Skin Cells
Sebaceous glands can produce too much oil, mixing with dead skin. This mix can clog pores, leading to acne. If skin isn’t cleaned regularly, blockages become more common.
Using salicylic acid and retinoids can be effective. They help remove dead skin and stop blockages from forming.
Bacterial Growth in Clogged Pores
Clogged pores are great places for bacteria to grow. Bacteria cause inflammation and acne. Good skincare fights both clogged pores and bacteria.
Using products with benzoyl peroxide helps target bacteria. It’s vital to keep the skin clean to limit bacteria growth.
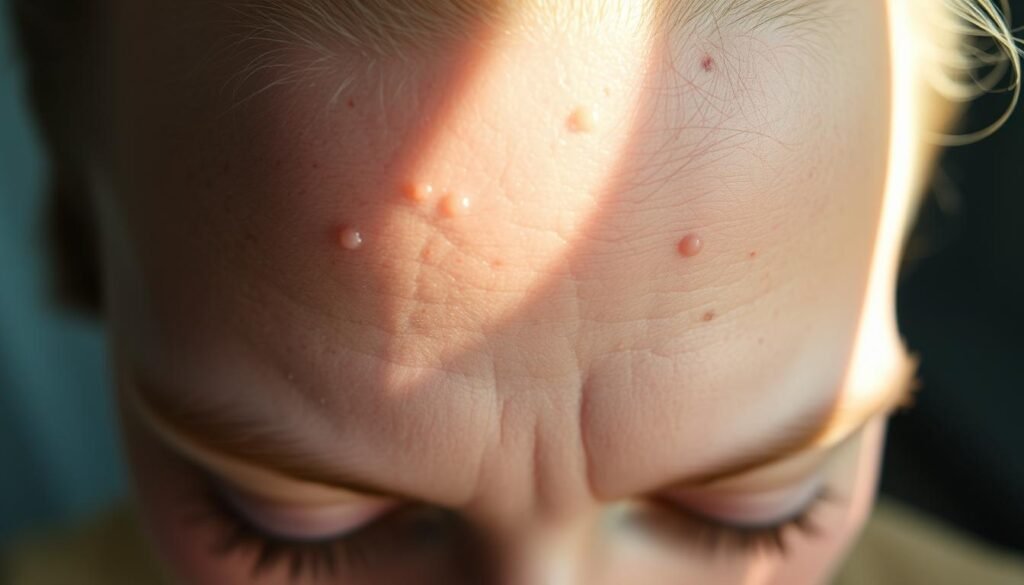
The Impact of Stress and Diet
Stress and diet are key in managing acne. Stress itself doesn’t cause acne. Yet, it can make it worse. It leads to more oil on the skin, hence more acne.
Knowing this can help improve skin health. Similarly, some foods make acne worse. Knowing which foods can affect your acne is crucial. It helps you choose better for clearer skin.
Stress as a Trigger for Acne
Studies show that more stress can mean worse acne. It can slow down the healing of acne. Reducing stress through yoga or hobbies can help. It benefits both your mind and skin.
Dietary Factors Contributing to Breakouts
What you eat can affect your acne. Foods that are high in sugar might cause acne. Avoiding these foods is good for your skin. Eating well supports not just your skin, but your whole health.
| Food Type | Recommended | Avoid |
|---|---|---|
| Fruits & Vegetables | Fresh, whole fruits and leafy greens | Processed versions with added sugars |
| Grains | Whole grains like quinoa and brown rice | White bread and pastries |
| Dairy | Almond or oat milk | High-fat dairy products |
| Fats | Healthy fats from avocados and nuts | Trans fats found in fast food |
Environmental Factors and Their Effects
Learning about how the environment affects skin health shows us how stuff like air quality and weather can spark acne. Things like humidity and pollution really do change our skin health, making acne worse. By understanding this, we can better handle acne.
Humidity and Pollution Levels
When it’s very humid, our skin gets oilier and we sweat more, which can make acne flare up. This makes it easy for bacteria to grow and block our pores. Also, pollution ties closely to acne since dirty air dries out our skin and irritates it. This combo forces us to look after our skin more.
Skin Irritation from Environmental Stressors
Things around us can irritate our skin, making managing acne even harder. Being around a lot of pollution can make our skin more irritated, worsening acne. It’s key to keep our skin healthy in these conditions. We should cleanse regularly and use products that don’t clog pores to protect our skin’s moisture against these harms.
For more information on how the environment influences acne, visit this link.

The Influence of Hair Products
Hair products can majorly affect acne, especially on the forehead. Lots of styling items have ingredients that may clog up pores or bother the skin. Knowing how these items connect to hair products and acne is key for good skincare.
Common Hair Products that Cause Acne
Many hair care products can spark acne breakouts. This leads to a condition called acne cosmetica. Often blamed products include:
- Pomades: Rich in oils, they can cause pomade acne when they touch the skin.
- Gels and Waxes: Like pomades, they leave sticky remains that may block pores.
- Conditioners: If not completely washed out, their heavy formulas can also lead to acne from styling products.
Ingredients like petroleum, silicone, and certain oils such as jojoba and coconut are particularly bad for those prone to acne.
Pomade Acne Explained
Pomade acne happens when oils from hair products touch the forehead and cause breakouts. Oils and silicones in these products can block pores. This can result in blackheads, whiteheads, and inflamed cysts. Acne from hair products tends to clear up about six weeks after stopping the products.
To minimize breakouts, try silicone and sulfate-free shampoos with organic ingredients. Also, non-comedogenic shampoos help prevent clogged pores. Adding products with salicylic acid removes residue that leads to acne. Showering at night also helps reduce oil transfer from hair to pillow, then to skin.
Women are more likely to get adult acne than men, with up to 22% affected. Knowing the types of hair products and their ingredients is crucial for clear skin.
Medication and its Side Effects
Understanding how medications link to acne is key for those wanting clearer skin. Some drugs can cause or make acne worse through their side effects. Know which ones can do this to make better choices about your care.
Types of Medications Linked to Acne
Various medications are tied to acne, such as:
- Corticosteroids: These can cause acne-like eruptions, especially if used in large doses or through IV.
- Lithium: This mood-stabilizer may lead to rare acne issues.
- Anticonvulsants: Though uncommon, they can cause acne breakouts.
- Hormonal Contraceptives: Drugs that change hormone levels can cause real acne.
- Vitamin B12 and Antibiotics: These are also known to cause acne.
Managing Medication-Induced Breakouts
If your medication causes acne, talk to health experts. Here’s how to deal with it:
- Talk to a dermatologist or your doctor about your symptoms and other options.
- Only stop the medication with a professional’s help.
- Sometimes, oral antibiotics or skin creams might be suggested to help your skin.
Often, acne from drugs goes away when you stop the medication. Keep an eye on how your skin reacts to new products. Don’t change your meds without asking a doctor. Also, be careful about allergic reactions to skin treatments.
| Medication Type | Potential Acne Side Effects | Management Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Corticosteroids | Acneiform eruptions on chest and back | Consult healthcare provider for alternatives |
| Lithium | Uncommon acne outbreaks | Seek advice for managing symptoms |
| Hormonal Contraceptives | Induces true acne due to hormonal changes | Discuss switching to alternative options |
| Anticonvulsants | Possible acne-like symptoms | Monitor skin health closely |
| Vitamin B12 | Linked to acne breakouts | Review dietary supplements with a doctor |
Cosmetic Reactions and Skin Irritation
Many people have acne because of cosmetics and some clothing. Knowing what causes these problems can help stop and control breakouts.
Makeup and Forehead Acne
Using different makeup products can cause reactions on the forehead. A study with over 900 participants found more than a third had reactions. Fragrances and preservatives in items like moisturizers and eyeshadows are common makeup irritants. They can cause dermatitis, with symptoms like redness and blisters.
To lower the risk of makeup causing acne, pick non-comedogenic products. Try patch testing before using them fully. But, even products labeled as hypoallergenic or dermatologist-tested might trigger reactions.
Clothing and Accessories Affecting the Skin
It’s easy to forget how clothing can cause acne. Tight hats and scarves can rub the skin, causing irritation and pimples. This can get worse with clothing that has certain chemicals or dyes.
Knowing what’s in your clothes and makeup can really help with acne. Using products with fewer ingredients may reduce skin problems. For tips on controlling acne triggers, visit this guide.
Hygiene Habits That Can Worsen Acne
Maintaining good hygiene is key for those worried about acne. A daily skincare routine clears impurities and helps manage breakouts. Knowing which habits can make acne worse is vital.
The Importance of Clean Skin
Washing your face twice a day with a gentle cleanser is important. This step removes oils and dirt that could block pores. But, washing too much can irritate your skin and increase oil production.
Exfoliate just once or twice a week to avoid skin damage and worse acne. Also, keeping your hair clean can stop breakouts along the hairline and neck. This is because oil from your hair can move to your skin.
Avoiding Touching the Face
Touching your face often can bring bacteria and dirt that cause acne. Not picking at pimples stops them from becoming open wounds that let bacteria in. To lower this risk, keep your hands off your face. Also, keep your phone screen and makeup brushes clean.
Choosing healthy ways to deal with stress can help prevent acne too. Understanding these points can improve your acne care plan.

Conclusion
Learning about the causes of forehead acne can help folks manage it better. With so many people, especially teens, seeing a doctor for this issue, it’s clear it’s a common concern. To prevent it, you need to recognize hormonal shifts, stick to a skincare routine, and make smart lifestyle choices.
Trigger factors like stress, certain hair products, and what you eat play a big role in causing acne. Dermatologists might recommend products with benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid. Yet, washing your face twice daily and keeping your hair clean are key habits to stop acne from forming.
To really improve your skin, blend diet changes, manage stress, and pick the right skincare products. This approach doesn’t just cut down on acne. It makes your skin healthier and better overall.